Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, And Types
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where the body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively, resulting in high levels of glucose in the blood. Understanding diabetes is important for the proper management of the condition, as it allows one to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and health.
Causes: There are two main types of diabetes – type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks and destroys the cells that produce insulin. The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is still unknown, but it is believed to be partly genetic and partly environmental. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, such as obesity, lack of exercise, and poor diet.
Symptoms: The symptoms of diabetes may vary depending on the type. Some common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, fatigue, and unintended weight loss. Type 2 diabetes may not have any symptoms in its early stages, but as the condition progresses, one may experience frequent infections, slow-healing wounds, blurred vision, and numbness in the extremities.
Types: As mentioned earlier, there are two main types of diabetes – type 1 and type 2. However, there are also other types of diabetes, such as gestational diabetes, which occurs during pregnancy, and monogenic diabetes, which is a rare form of diabetes caused by a single gene mutation.
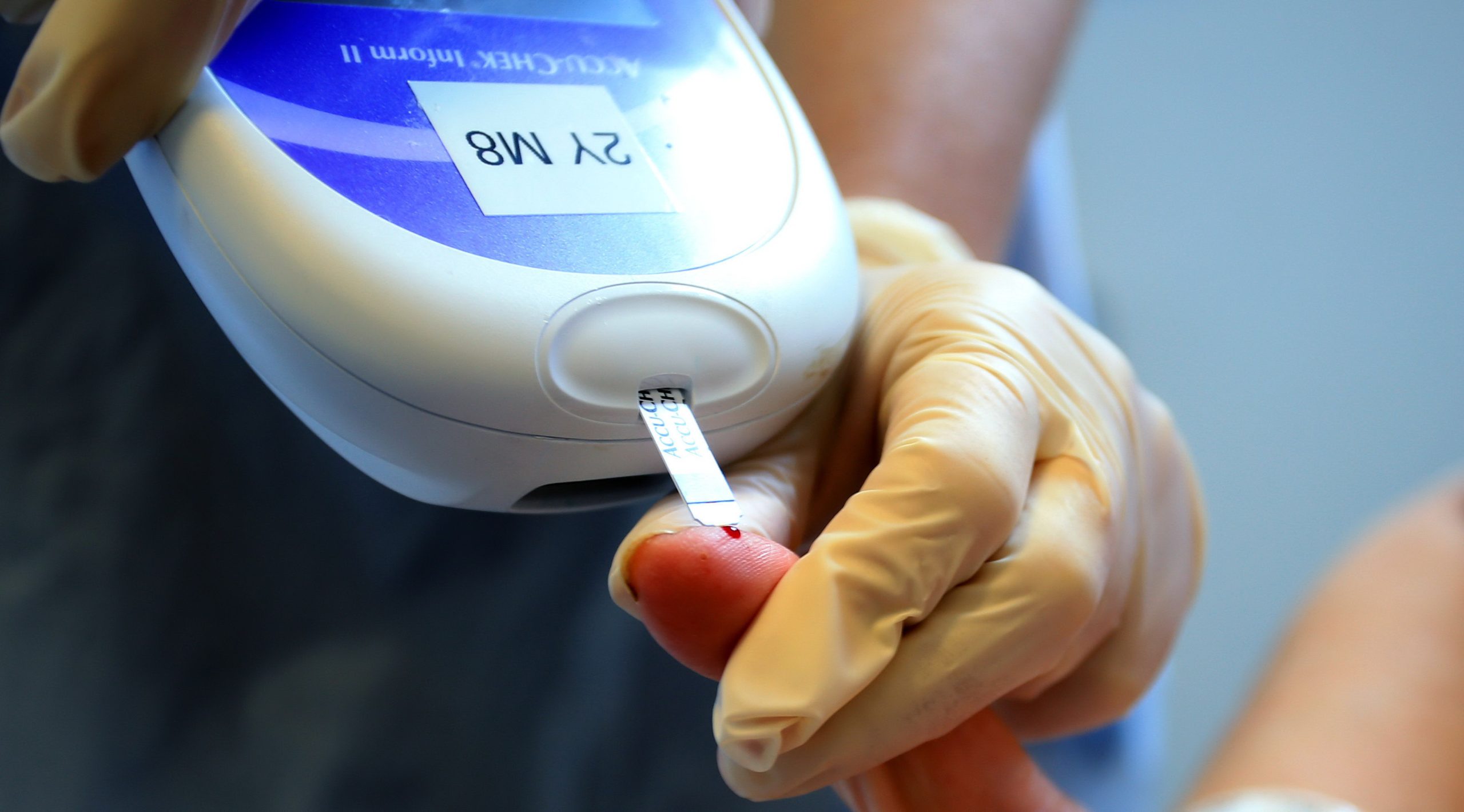
Tips For Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels At Home
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition that requires constant monitoring and maintenance to keep it under control.
One of the essential aspects of diabetes management is keeping track of blood glucose levels regularly. Monitoring blood glucose levels is crucial as it helps to detect if the sugar levels are too low or too high. It also helps in identifying patterns that can be used to adjust medications, diet, and exercise routine.
Here are some useful tips for monitoring blood glucose levels at home:
- Invest in a good quality blood glucose monitor: A reliable glucose monitor is a must-have for every person with diabetes. Several types of glucose monitors are available that can give accurate readings. Choose a meter that suits your lifestyle, and follow the instructions on how to use it correctly.
- Wash your hands: Before checking your blood glucose levels, ensure your hands are clean and dry. Clean your finger with alcohol and let it dry before pricking it to collect the blood.
- Record your results: Keeping a record of blood glucose levels is necessary to monitor the treatment progress. Record the readings in a logbook or on a smartphone app. This way, you can easily discuss the results with your healthcare provider at regular check-ups.
- Check levels often: People with diabetes should check their blood glucose levels regularly as advised by their healthcare team. It is especially important to monitor after meals, before bed, before and after exercise, when feeling unwell, or when there is a change in routine or medication.
- Understand the results: Knowing what the blood glucose levels mean is crucial in making informed decisions about diabetes management. Your healthcare provider can help you understand what the readings mean and what actions to take if the results are too high or too low.
By keeping a regular check on blood glucose levels, people with diabetes can maintain better control over their condition. Follow the tips above and discuss any concerns about monitoring with your healthcare provider.
Developing A Balanced And Healthy Diet For Diabetes Management
Include Complex Carbohydrates
Incorporate Lean Proteins
Avoid Processed Foods
Eat at Regular Intervals
Stay Hydrated
Incorporating Exercise İnto A Diabetes Management Plan
When it comes to managing diabetes, diet and medication are often at the top of the priority list. But did you know that exercise can also be a crucial component of staying healthy and managing blood sugar levels? Here are some tips for successfully incorporating exercise into your diabetes management plan.
Consult your healthcare provider first. Before starting any exercise routine, it’s important to talk with your doctor or diabetes educator. They can help you determine what types of exercise are safe and appropriate for you, as well as how to adjust medication or insulin doses if needed.
Choose enjoyable activities. Exercise doesn’t have to mean hitting the gym or running on a treadmill. There are plenty of activities that can get your heart rate up and provide health benefits, such as walking, dancing, swimming, or biking. The key is to choose something you enjoy so that it feels less like a chore and more like a fun activity.
Start slowly and gradually increase intensity. If you’re new to exercise or haven’t done much physical activity in a while, it’s important to start slowly and build up gradually. You might begin with just 10-15 minutes of activity per day, gradually increasing duration and intensity over time. This can help prevent injury and avoid overexertion.
| Exercise Type | Frequency | Duration | Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Walking | 5-7 days per week | 30-60 minutes | Brisk pace |
| Weight training | 2-3 days per week | 20-30 minutes | Light to moderate |
| Cycling | 3-5 days per week | 30-60 minutes | Moderate to high |
Monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise. Exercise can affect blood sugar levels, so it’s important to check them regularly and adjust accordingly. You might also consider carrying a snack or glucose tablets with you in case of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Make exercise a regular habit. Consistency is key when it comes to reaping the benefits of exercise. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity most days of the week. By making exercise a regular part of your routine, you’ll not only improve your diabetes management, but also your overall health and well-being.
Exploring Medication Options For Diabetes Treatment
Diabetes is a chronic condition that millions of people all around the world live with every day. While lifestyle changes like diet and exercise can play a crucial role in diabetes management, there are several medication options that can also help keep blood sugar levels in check. It is essential to understand the various types of medication available and how they work in treating diabetes.
One common medication for diabetes is insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels by moving glucose from the bloodstream into cells. People with type 1 diabetes, who do not produce insulin naturally, must take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to maintain stable blood sugar levels. For some with type 2 diabetes, insulin may also be necessary to help control blood sugar levels.
Oral medication is another option for people with type 2 diabetes who struggle to maintain stable blood sugar levels through diet and exercise alone. Metformin is often the first type of oral medication recommended by doctors. It works by decreasing the amount of glucose produced by the liver and helping the body use insulin more effectively.
Other types of oral medication include sulfonylureas, meglitinides, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, and thiazolidinediones. Sulfonylureas and meglitinides work by stimulating insulin production, while alpha-glucosidase inhibitors and thiazolidinediones help the body use insulin more efficiently.
It is important to note that all medications come with potential side effects and risks. For example, some diabetes medication may cause low blood sugar levels or interact with other medications. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the best medication option for individual needs and to closely monitor blood sugar levels while taking medication.
In conclusion, exploring medication options is an important step in diabetes management. While lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are vital in diabetes treatment, medication can help control blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Working closely with a healthcare provider to find the appropriate medication and closely monitoring blood sugar levels can help manage diabetes effectively.
Dealing With Common Diabetes Complications, Such As Neuropathy And Retinopathy
Diabetes is a condition that affects millions of people all over the world. It occurs when there is too much glucose in the blood, which can lead to a range of complications. Two common complications of diabetes are neuropathy and retinopathy. Neuropathy is a condition where there is damage to the nerves in the body, while retinopathy is damage to the blood vessels in the eye that can cause blindness.
Neuropathy is a common complication of diabetes that can affect the feet, legs, and hands. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, or burning pain in these areas. It can also cause muscle weakness, and in severe cases, it can affect the digestive system, bladder, and heart.
Retinopathy, on the other hand, is a complication that affects the eyes. It happens when high blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels in the retina. Symptoms include blurry or distorted vision, difficulty seeing at night, and even blindness.
The good news is that there are steps you can take to prevent and manage these complications. The best way to prevent neuropathy and retinopathy is to keep your blood sugar levels under control. This can be achieved through a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and taking any medications as prescribed by your doctor.
For those already dealing with neuropathy or retinopathy, there are several treatments available. Medications can be prescribed to manage the symptoms of neuropathy, such as pain and muscle weakness. For retinopathy, laser surgery can be used to slow down or stop the progression of the disease.
It’s important to have regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor these complications and catch any issues early on. Additionally, it’s crucial to take care of your overall health and well-being by managing stress, getting enough sleep, and quitting smoking if you haven’t already.
In conclusion, neuropathy and retinopathy are common complications of diabetes that can significantly impact your quality of life if not managed properly. However, with the right care and attention, you can prevent these complications from occurring and effectively manage them if they do occur.
Coping With Emotional Challenges Of Living With Diabetes
Living with diabetes can be an emotional roller coaster. It can be overwhelming and frustrating to constantly manage blood sugar levels, injections, and medications. Yet, the emotional challenges that come with diabetes management are often overlooked. For people with diabetes, it is not just about managing their physical health, but also their mental and emotional well-being.
One of the most common emotional challenges for someone with diabetes is the constant worry and anxiety over their health. Fear of complications, such as neuropathy or blindness, can be debilitating. Concerns about low blood sugar levels, especially during physical activities or when driving, can also add to the stress level of someone managing diabetes.
Another emotional challenge faced by people with diabetes is depression. Studies have shown that people with diabetes are twice as likely to develop depression than those without diabetes. Diabetes can impact every aspect of life, from relationships to work, leading to feelings of helplessness and hopelessness.
- Feeling isolated and alone is another emotional challenge that people with diabetes often face. For many, it can feel like no one else truly understands what they are going through. However, it is essential to know that there are support groups and diabetes communities available to provide a source of encouragement and motivation to help navigate the ups and downs of living with diabetes.
Dealing with diabetes management on a daily basis can be stressful, leaving someone feeling drained and fatigued. This constant state of stress can lead to burnout, which can make it difficult to maintain healthy diabetes management habits.
Fortunately, there are steps that can be taken to manage the emotional challenges of living with diabetes. One of the most effective ways to deal with this is to seek support. This could be in the form of talking to a friend, joining a support group or seeking professional help from a mental health counselor. It’s important to make emotional well-being a priority as well as physical health.
Living with diabetes can be a challenging experience. However, support from healthcare providers, family, friends, and diabetes communities can help manage the emotional challenges associated with diabetes. Remember, you are not alone and it is okay to ask for help. Managing emotions effectively will contribute to better physical and mental health outcomes.
Finding Support And Community Through Diabetes Organizations And Groups
Diabetes can be a stressful and overwhelming disease to manage. It’s important to know that you don’t have to face it alone. There are many resources available to provide support and guidance throughout your journey with diabetes.
One of the best sources of support is diabetes organizations and groups. These organizations offer a community of individuals who are going through similar experiences and can provide invaluable support and advice. They also offer educational resources, advocacy efforts, and fundraising opportunities.
There are numerous diabetes organizations and groups to choose from, both locally and nationally. Some of the most well-known organizations include the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation (JDRF). Both of these organizations offer a wealth of resources and support for individuals living with diabetes.
Local diabetes groups can also be a great source of support. They offer the opportunity to connect with individuals in your community who are dealing with similar challenges. These groups often meet regularly and provide a safe space to share experiences and offer support.
- Make a list of diabetes organizations and groups in your area and reach out to them to see what resources they offer.
- Attend local support group meetings to connect with others who are living with diabetes.
- Participate in fundraising or advocacy efforts to give back to the diabetes community.
Remember, you don’t have to navigate diabetes alone. There are many resources available to provide support and guidance. Connect with diabetes organizations and groups to find the community you need to thrive.
Navigating Social Situations And Dining Out With Diabetes
Living with diabetes means that many things that were once routine now require extra thought and attention. One of the most challenging aspects of diabetes management can be navigating social situations and dining out. While it may seem difficult at first, with a bit of planning and preparation, it is possible to enjoy dining out with friends and family while also managing your diabetes.
One of the first steps in navigating social situations and dining out with diabetes is to plan ahead. Before visiting a restaurant or attending a social event where food will be served, take a look at the menu or inquire about what will be served. This will allow you to make informed decisions about what to eat and to plan accordingly.
In addition to planning ahead, it is important to be mindful of portion sizes and carbohydrate content. Many restaurants offer large servings of high-carbohydrate foods, which can make it difficult to control blood sugar levels. One way to address this issue is to split a meal with a dining partner, or to ask for half of your meal to be packaged to-go before it is served. Another option is to choose menu items that are lower in carbohydrates or to modify your order to reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed. For example, choosing a salad with a protein source and asking for dressing on the side can be a great way to enjoy a meal while also managing your diabetes.
Finally, it is important to remember that managing diabetes is not just about what you eat, but also how you manage stress and emotions. Dining out with friends and family can be stressful, particularly if you are worried about managing your diabetes in a social setting. One way to address this is to communicate your needs and concerns with your dining partners ahead of time, and to make a plan for managing your diabetes together.
In conclusion, navigating social situations and dining out with diabetes can be a challenge, but with a bit of planning and preparation, it is possible to enjoy dining out while also managing your diabetes. By planning ahead, being mindful of portion sizes and carbohydrate content, choosing lower-carbohydrate menu items, and managing stress and emotions, you can successfully navigate social situations and enjoy dining out with friends and family.
Understanding The Importance Of Self-Care İn Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people around the world. It is a disease that affects how our bodies use glucose, the main source of energy for our cells. When you have diabetes, your body is either not producing enough insulin or is not using it correctly. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose enter the cells of our body to be used for energy, but in diabetics, glucose builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels that can cause serious health complications over time.
While there are many different types of diabetes and several factors that contribute to its development, one key component of managing diabetes is self-care. Self-care involves taking daily actions to manage blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and maintain overall health and wellbeing. Self-care can include monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, following a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, taking prescribed medications, and managing stress effectively, among other things.
Self-care is critical because it helps diabetics stay in control of their condition, avoiding both short- and long-term complications. Short-term complications of uncontrolled blood sugar levels can include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), while long-term complications can include heart disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, and vision loss. Through self-care practices, diabetics can minimize their risk of these complications and maintain their quality of life.
| Self-Care Practices for Diabetes Management |
|---|
| Monitor blood sugar levels regularly: Checking blood sugar levels multiple times per day can help diabetics stay within their target range and make adjustments to medication, diet or exercise as needed. |
| Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This includes eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats, while limiting processed foods, saturated and trans fats, and added sugars. |
| Get regular physical activity: Physical activity not only helps manage blood sugar levels but also reduces the risk of developing long-term complications of diabetes such as heart disease and neuropathy. |
| Take medications as prescribed: Medications such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents are an essential part of diabetes management and should be taken according to a healthcare provider’s instructions. |
| Manage stress effectively: Chronic stress can negatively affect blood sugar levels and overall health. Techniques such as deep breathing, yoga, and meditation can help manage stress levels. |
By practicing self-care, diabetics can not only improve their health but also enhance their quality of life. Taking control of one’s condition can also help reduce the emotional challenges of living with diabetes, including depression, anxiety and frustration. Understanding the importance of self-care is an essential part of diabetes management, and with proper support and guidance, diabetics can maintain their health and wellbeing over time.
Medical Treatment: The New Revolution